Project Management Tool Software
Home > Page
What is project management?
Project management is the application of knowledge, skills, tools, and techniques to project activities to meet the project requirements. It involves planning, organizing, and managing resources to bring about the successful completion of specific project goals and objectives. The process typically involves the following phases:
- Initiation: Defining the project at a high level and obtaining authorization.
- Planning: Establishing the scope, objectives, and course of action required to attain the project goals.
- Execution: Performing the work defined in the project management plan to meet the project objectives.
- Monitoring and Controlling: Tracking, reviewing, and regulating the progress and performance of the project. Identifying any areas where changes to the plan are required and initiating those changes.
- Closing: Finalizing all project activities to formally close the project or phase.
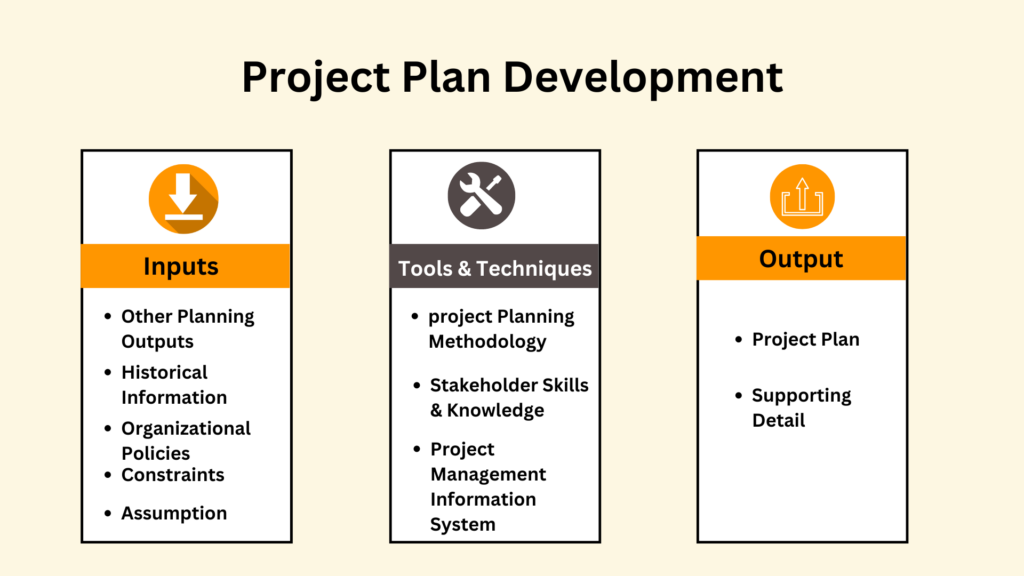
Benefits of Project management tool Software:
Project management tool software offers a variety of benefits that can enhance productivity, improve collaboration, and ensure projects are completed on time and within budget. Here are some key advantages:
Improved Organization and Planning:
- Task Management: Helps in breaking down large projects into smaller, manageable tasks, making it easier to assign and track them.
- Scheduling: Facilitates the creation of timelines and schedules, ensuring that deadlines are met.
Enhanced Collaboration:
- Team Communication: Provides platforms for team members to communicate in real-time, share updates, and collaborate on documents.
- File Sharing: Allows easy sharing and access to project-related files and resources.
Increased Accountability and Transparency:
- Task Assignments: Clearly assigns tasks and responsibilities, ensuring everyone knows their role.
- Progress Tracking: Offers tools to monitor the progress of tasks and the overall project, providing transparency.
Better Resource Management:
- Resource Allocation: Helps in efficiently allocating resources like team members, budget, and equipment.
- Workload Management: Ensures that workload is evenly distributed, preventing burnout and overworking of team members.
Risk Management:
- Risk Identification: Aids in identifying potential risks early in the project.
- Mitigation Planning: Facilitates the development of strategies to mitigate or manage risks.
Time and Cost Efficiency:
- Time Tracking: Tracks the time spent on tasks, helping in better time management and ensuring deadlines are met.
- Budget Tracking: Monitors expenses and ensures the project stays within budget.
Improved Reporting and Analytics:
- Progress Reports: Generates detailed reports on project progress, task completion, and team performance.
- Data Analytics: Analyzes project data to provide insights and improve future project planning and execution.
Scalability:
- Customizable: Can be tailored to fit projects of different sizes and complexities.
- Integration: Often integrates with other tools and software, enhancing its functionality and adaptability.
Customer Satisfaction:
- Deliverables: Ensures that project deliverables are completed on time and meet quality standards, leading to higher customer satisfaction.
- Feedback: Provides platforms for gathering and incorporating customer feedback throughout the project lifecycle.
Remote Work Facilitation:
- Access Anywhere: Enables team members to access the project details and collaborate from any location, which is crucial for remote work setups.
How to Use It :
Using project management tool software typically involves several steps, from initial setup to ongoing project management. Here’s a general guide on how to use it effectively:.
Selection and Setup
1.Choose the Right Tool:
Assess your needs and choose a project management tool that fits your project requirements and team size (e.g., Trello, Asana, Monday.com, Jira).
Sign up for the software and create an account. Some tools offer free trials or freemium versions.
2. Set Up Your Workspace:
- Create a workspace or project space where all project activities will be managed.
2. Project Planning
- Define the Project:
Outline the project scope, objectives, and deliverables. Create Tasks and Subtasks:
Break down the project into smaller tasks and subtasks. Assign each task a clear title and description.Assign Tasks:
Allocate tasks to team members based on their roles and responsibilities.Set Deadlines:
Establish deadlines for each task and subtask to ensure timely completion.
3. Resource Management
Allocate Resources:
Assign resources (team members, budget, equipment) to tasks as needed.Manage Workload:
Use workload management features to ensure tasks are evenly distributed among team members.
4. Collaboration and Communication
Set Up Communication Channels:
Use built-in chat, comment, or messaging features to facilitate team communication.Share Files and Documents:
Upload and share relevant documents, files, and links within the project workspace.Hold Meetings:
Schedule regular meetings to discuss progress, challenges, and next steps.
5. Tracking and Monitoring
Track Progress:
Use dashboards and progress bars to monitor the status of tasks and the overall project.Update Tasks:
Regularly update the status of tasks (e.g., in progress, completed) to keep everyone informed.Use Gantt Charts/Calendars:
Utilize Gantt charts or project calendars to visualize timelines and dependencies.
In summary, project management tool software streamlines project planning, enhances team collaboration, and improves resource management, making it essential for modern project execution. By carefully selecting and setting up the tool, planning projects meticulously, and utilizing its features for tracking, reporting, and risk management, teams can achieve higher efficiency and better project outcomes. Regular training, clear guidelines, and adaptability further ensure the successful integration and use of the software, ultimately leading to the timely and cost-effective completion of projects.
Also Read – Accounting & Finance Software

